Google has embarked on a pioneering initiative aimed at confronting one of the most pressing challenges faced by millions worldwide: flood prediction.
This initiative represents a significant shift in focus for Google, which had previously collaborated with Apollo Hospitals in India to spearhead advancements in early disease detection through AI technologies.
Now, turning their expertise towards environmental challenges, Google’s researchers are delving into the complex realm of hydrological phenomena with the aim of developing sophisticated AI-driven models for flood forecasting.
The urgency and importance of this endeavor are underscored by a recent research paper published in the prestigious journal Nature.
This publication illuminates the innovative methodologies and the potential impact of AI in revolutionizing flood forecasting, highlighting Google’s commitment to not only advancing technology but also applying it in ways that can save lives and mitigate the adverse effects of climate change.
The initiative is a key component of Google’s broader Adaptation and Resilience efforts, reflecting a deep-seated commitment to harnessing technology in the battle against global environmental challenges.
Through the development of highly accurate hydrological simulation models, Google aims to outperform traditional methods of flood prediction, offering hope for a future where communities around the globe are better prepared to face the threats posed by rising water levels.
Google’s Approach to Flood Prediction
Google’s approach to enhancing flood prediction capabilities centers around the innovative application of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence technologies.
Recognizing the limitations of traditional flood forecasting methods, Google researchers have embarked on developing advanced hydrological simulation models that promise unprecedented accuracy in predicting flood events.
This effort is part of Google’s wider Adaptation and Resilience initiatives, aimed at combating climate change and improving global preparedness against natural disasters.
At the core of Google’s methodology is the use of machine learning techniques to develop sophisticated hydrological simulation models.
These models are built upon the foundations of the Global Flood Awareness System version 4, which is operated by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts.
By leveraging GloFAS and incorporating AI, Google’s models can cover a broader range of flood events, providing earlier and more precise predictions than traditional river prediction methods.
A crucial component of Google’s AI model is the implementation of long short-term memory networks. These networks are designed to predict daily streamflow across a seven-day forecast horizon with remarkable accuracy.
LSTM networks are trained on a vast dataset gathered from 5680 streamflow gauges worldwide, employing a rigorous “random k-fold cross-validation” method. This approach ensures that the models are robust and capable of generalizing across different geographical and climatic conditions.
Google’s research and development efforts culminate in the Flood Hub system, a comprehensive platform that delivers river predictions for 80 countries up to seven days in advance.
The Flood Hub system is a testament to Google’s commitment to operationalizing its scientific findings into practical, real-world applications. By providing timely and accurate flood forecasts, the system aims to enable communities worldwide to better prepare for and mitigate the impact of floods.
The sophistication and accuracy of Google’s AI-driven flood forecasting models represent a significant leap forward in the field of hydrological research. By outperforming traditional flood prediction methods, these models offer a new paradigm in disaster preparedness and response.
The integration of AI and ML not only advances the scientific understanding of flood dynamics but also translates this knowledge into actionable insights that can significantly reduce the risk and impact of flood events on vulnerable communities around the globe.
Technology and Implementation
Google’s breakthrough in flood forecasting is a culmination of cutting-edge technology and strategic implementation designed to enhance global preparedness and resilience against flood-related disasters.
By integrating advanced machine learning techniques and artificial intelligence with hydrological science, Google has developed a system capable of delivering accurate and timely flood forecasts across the globe.
This section delves into the technological backbone and the implementation strategies that make Google’s flood forecasting initiative both innovative and impactful.
At the heart of Google’s flood prediction model lies the utilization of long short-term memory networks, a type of recurrent neural network tailored to recognize patterns in sequential data.
These LSTM networks are trained on an extensive dataset collected from 5,680 streamflow gauges worldwide. This enables the AI to learn from historical flood events and predict future occurrences with remarkable accuracy.
The training process employs a rigorous “random k-fold cross-validation” technique, ensuring the model’s robustness and reliability across diverse geographical locations and environmental conditions.
Google’s AI model is built upon sophisticated hydrological simulation models that integrate data from the Global Flood Awareness System version 4, operated by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts.
This foundation allows the AI to simulate a wide range of flood events, surpassing the capabilities of traditional river prediction methods. By harnessing the power of GloFAS alongside AI, Google’s models can predict floods with unprecedented precision, offering early warnings and detailed forecasts that can significantly aid in disaster preparedness.
The culmination of Google’s technological advancements is the Flood Hub system. This platform delivers actionable flood forecasts for 80 countries up to seven days in advance.
This system represents a significant operationalization of Google’s research findings, providing a real-time flood forecasting service that can alert communities to impending flood risks.
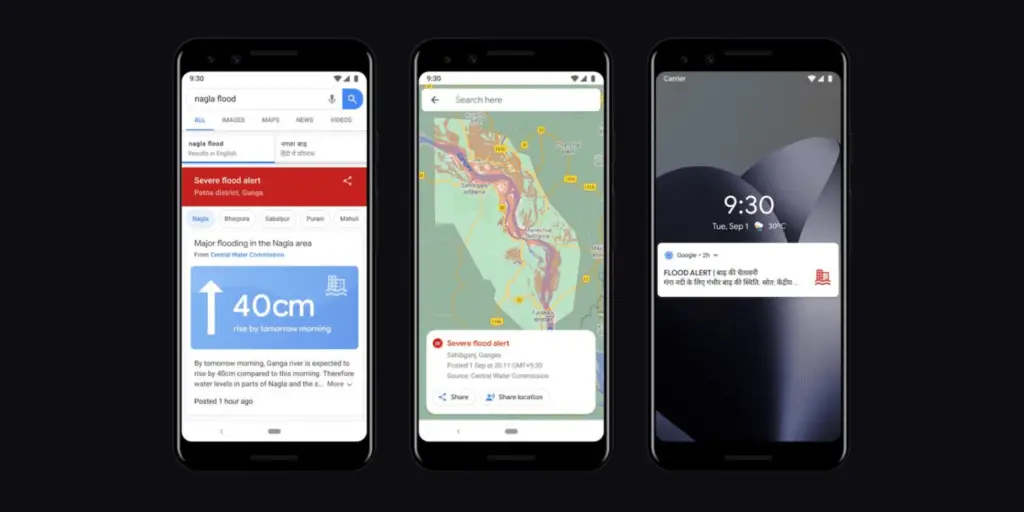
The Flood Hub is accessible through Google Search, Maps, Android notifications, and its dedicated platform, ensuring widespread dissemination of critical flood warnings.
Google’s implementation strategy extends beyond the development of advanced models to the practical application of these technologies in real-world scenarios.
The flood forecasting system is designed to serve a global audience, offering vital information that can help safeguard lives and reduce economic damages caused by flooding.
By providing forecasts through easily accessible digital platforms, Google ensures that communities, governments, and aid organizations can take anticipatory action to protect vulnerable populations.
Google’s flood forecasting initiative marks a significant step forward in leveraging technology to combat the impacts of climate change and natural disasters.
By making accurate flood forecasts available on a global scale, particularly in regions where data is scarce, and the risk of flooding is high, Google is contributing to a broader effort to enhance disaster resilience and climate adaptation.
This innovative application of AI and ML technologies sets a new standard for disaster preparedness, offering hope for a future where technology plays a central role in mitigating the human and economic toll of natural disasters.
Impact and Benefits
Google’s AI-powered flood forecasting initiative represents a monumental step forward in the global effort to mitigate the impacts of flooding. This natural disaster affects millions worldwide.
By harnessing the power of advanced machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies, Google has not only pushed the boundaries of scientific research in hydrology but also translated these innovations into practical solutions that have real-world applications.
The initiative’s impact and benefits stretch across various domains, from enhancing global resilience against climate change to providing communities with crucial lead time to prepare for impending floods.
Google’s flood forecasting system is a critical component of the company’s broader Adaptation and Resilience efforts aimed at combating climate change and its effects.
By providing accurate and timely flood predictions, Google helps reduce the vulnerability of communities worldwide, especially in regions where the threat of flooding is compounded by climate change.
The initiative’s ability to extend the reliability of global nowcasts from zero to five days represents a significant advancement in early warning systems, giving communities more time to implement disaster preparedness and evacuation plans.
Utilizing ML and AI, Google’s flood forecasting models outperform traditional methods by covering a broader range of flood events and delivering earlier and more precise predictions.
This improvement is particularly crucial in data-scarce regions and developing countries, where the lack of infrastructure and resources has historically impeded accurate flood forecasting.
Google’s initiative ensures that reliable flood-related data and forecasts are accessible in these vulnerable areas, leveling the playing field and offering protection to those who need it most.
One of the most immediate benefits of Google’s flood forecasting system is the dissemination of real-time alerts through widely used platforms like Google Search, Maps, and Android notifications.
This approach ensures that timely warnings reach a broad audience, enabling individuals and communities to take necessary precautions and minimize the impact of floods.
The availability of forecasts on the Flood Hub platform further enhances accessibility, allowing people, communities, governments, and aid organizations to take anticipatory action.
By providing communities with advanced notice of flood risks, Google’s initiative empowers individuals to safeguard their lives, properties, and livelihoods.
Early warning systems significantly reduce fatalities and economic losses associated with floods, enabling better preparedness and more effective response efforts.
The initiative’s focus on extending forecasts to previously underserved regions ensures that the benefits of AI-powered flood forecasting are shared globally, contributing to a more equitable distribution of technology’s lifesaving potential.
Google’s flood forecasting initiative not only advances the field of hydrological research but also fosters collaboration between the tech industry, academic community, and governmental organizations.
By sharing insights and methodologies, Google encourages the exchange of knowledge and best practices, stimulating further research and innovation in flood forecasting and climate resilience.
This collaborative approach amplifies the initiative’s impact, paving the way for new breakthroughs and the development of more sophisticated disaster prediction and mitigation technologies.
Challenges and Solutions
Google’s AI-powered flood forecasting initiative, while groundbreaking, has not been without its challenges. These hurdles stem from the inherent complexities of predicting natural disasters, the limitations of existing data, and the logistical difficulties of implementing technology-based solutions across diverse global landscapes.
Yet, Google’s journey from conceptualization to the deployment of its flood forecasting system exemplifies how innovative approaches and strategic collaborations can overcome such obstacles.
One of the most significant challenges in developing accurate flood forecasting models is the scarcity and varying quality of hydrological data, especially in developing countries.
Many regions most vulnerable to flooding lack the infrastructure for collecting comprehensive streamflow data, which is crucial for traditional flood prediction methods.
The computational complexity of simulating flood events accurately across different terrains and climatic conditions presents another challenge. Traditional hydrological models require significant computational resources and a sophisticated understanding of local geographies, which can be a barrier to scaling solutions globally.
Making the transition from accurate predictions to timely and accessible alerts for the general population involves logistical challenges, including ensuring that forecasts are understood and acted upon by communities at risk.
To address the issue of data scarcity, Google turned to machine learning and artificial intelligence, specifically long short-term memory networks, which can predict flood events by learning from patterns in extensive datasets.
By training these models on data from thousands of streamflow gauges and employing “random k-fold cross-validation,” Google’s system can offer reliable forecasts even in regions lacking local data.
Google developed advanced hydrological simulation models built upon the Global Flood Awareness System and enhanced by AI.
These models outperform traditional methods by covering a broader range of flood events and providing more precise predictions, thus overcoming the computational challenges associated with flood forecasting.
To ensure that its flood forecasts reach and benefit those in need, Google has implemented a multi-platform dissemination strategy. Flood warnings and forecasts are made available through Google Search, Maps, Android notifications, and the dedicated Flood Hub platform, ensuring widespread accessibility and timely distribution of crucial information.
Google’s initial pilot in India’s Patna region, part of the flood-prone state of Bihar, was instrumental in learning valuable lessons about local data utilization and model accuracy.
Collaborating with local governments and integrating real-time data, Google refined its forecasting models to be more region-specific.
Google’s ongoing collaborations with academic researchers, international organizations, and the scientific community have been vital in scaling the solution globally and ensuring its effectiveness across different regions.
Acknowledging the dynamic nature of climate change and its impact on flood patterns, Google continues to refine its models and explore new collaborations to enhance the accuracy and reach of its flood forecasting system.
The initiative’s evolution demonstrates Google’s commitment to using technology to address complex global challenges, setting a precedent for how tech companies can contribute to disaster resilience and climate adaptation efforts.
As Google expands its flood forecasting to cover more types of flood-related events and regions, its journey offers valuable insights into overcoming the challenges inherent in leveraging technology for environmental and humanitarian benefits.
Future Directions and Collaborations
As Google’s AI-powered flood forecasting initiative continues to evolve, its future directions and collaborations are set to expand the impact and reach of this groundbreaking work.
Building on the successes and lessons learned from initial implementations, Google aims to further harness technology to mitigate the effects of climate change, particularly through improved flood forecasting and response mechanisms.
The initiative’s trajectory indicates a broadening scope, not only in terms of geographical coverage but also in the diversity of its collaborations and the technological advancements it seeks to integrate.
One of the primary future directions for Google’s flood forecasting initiative is the expansion of its geographical coverage, aiming to include more regions that are prone to flooding yet lack adequate forecasting systems.
This includes a concerted effort to bring high-accuracy forecasts to areas where data scarcity has historically made such predictions challenging.
Google is exploring ways to enhance its forecasting models to predict various types of flooding, such as flash floods and urban floods, which pose significant risks to densely populated areas.
Google plans to continue advancing the AI and machine learning technologies at the heart of its flood forecasting system.
This includes refining the LSTM networks and exploring new AI techniques that can improve the accuracy and timeliness of flood predictions.
Innovations in data processing and hydrological modeling will also play a crucial role in enabling the system to handle more complex forecasting scenarios and adapt to the changing climate patterns that affect flood dynamics.
Collaboration remains a cornerstone of Google’s strategy for enhancing its flood forecasting initiative. By working closely with international organizations, such as the World Meteorological Organization, Google aims to support global early warning systems and contribute to initiatives like the Early Warnings for All initiative.
Partnerships with local governments and national meteorological and hydrological services are crucial for integrating local data sources and expertise into Google’s forecasting models, ensuring that the forecasts are as accurate and relevant as possible.
Google recognizes the importance of academic and scientific contributions to advancing flood forecasting technology.
Continued collaboration with researchers and institutions around the world will help incorporate the latest hydrological insights and technological innovations into Google’s models.
These partnerships also facilitate the sharing of knowledge and best practices, driving collective progress in the field of disaster preparedness and climate resilience.
Looking ahead, Google aims to broaden the initiative’s impact by not only predicting floods but also offering solutions and recommendations for mitigation and response.
This could include integrating flood forecasts with other Google services to provide actionable advice to individuals and communities at risk.
Google is exploring ways to use its platform and technologies to address other climate adaptation challenges, reflecting a holistic approach to leveraging technology in the fight against climate change.
Final Thoughts
Google’s foray into AI-powered flood forecasting marks a significant leap towards leveraging technology for societal benefit, particularly in the realm of disaster preparedness and climate change resilience.
By harnessing the capabilities of artificial intelligence and machine learning, Google has not only advanced the scientific understanding of flood dynamics but also translated these insights into practical, actionable tools that communities worldwide can rely on for early warning and preparedness.
The initiative’s journey from concept to implementation illustrates the profound potential of combining technological innovation with strategic collaboration.
Through partnerships with local governments, international organizations, and the academic community, Google has managed to overcome significant challenges related to data scarcity, computational complexity, and the accessibility of alerts.
These collaborations have been pivotal in refining the flood forecasting models and ensuring they are as accurate and inclusive as possible.
Looking ahead, Google’s commitment to expanding the scope and accuracy of its flood forecasting initiative promises to further enhance global resilience against flooding.
The planned expansion into new regions, the incorporation of additional types of flooding events, and ongoing technological enhancements underscore a forward-thinking approach to disaster preparedness.
The Initiative’s focus on broadening collaborations and integrating forecasts with actionable guidance for communities highlights a holistic strategy aimed at maximizing the impact of these technological advancements.
Google’s AI-powered flood forecasting initiative represents a remarkable example of how technology can be harnessed to address some of the most pressing challenges facing humanity today.
By continuing to innovate and collaborate, Google is setting a new standard for how tech companies can contribute to global efforts in disaster resilience and climate adaptation.
As this initiative evolves, it holds the promise of not only saving lives and protecting livelihoods but also inspiring further technological solutions to the myriad challenges posed by climate change.


