Perplexity is an AI-driven search platform known for its innovative approach to information retrieval. On May 31, 2024, Perplexity released its latest feature, ‘Pages,’ designed to revolutionize the way users conduct research and compile reports.
Perplexity’s ‘Pages’ is a new tool that promises to ease the burden of gathering information and creating comprehensive reports, making it particularly beneficial for educators, researchers, and hobbyists.
Perplexity’s ‘Pages’
Pages is a newly introduced feature by Perplexity, designed to simplify and enhance the process of conducting research and writing reports.
This tool allows users to create customizable webpages based on specific prompts, effectively automating the tasks of information gathering, content creation, and presentation layout.
- Customizable Webpages – Users can generate tailored webpages by simply inputting their topic or query into the prompt box. The tool then uses Perplexity’s advanced AI search models to gather relevant information and draft the content.
- Audience-Specific Writing – ‘Pages’ offers the ability to adjust the writing style to suit different audience types—beginners, experts, or a general audience. This ensures that the content is appropriate for the intended readers.
- Structured Content Creation – The tool organizes the gathered information into coherent sections, cites sources accurately and includes visuals to enhance understanding.
- Adjustable Detail and Visuals – Users can control the level of detail in the content and modify the visuals to better match their preferences or requirements.
- Editing Limitations – One notable limitation is that users cannot directly edit the generated text. Any corrections or adjustments must be made by submitting a new prompt.
Intended Audience
Educators – To develop comprehensive study guides and educational materials.
Researchers – create detailed reports on their findings.
Hobbyists – To share knowledge and insights on topics of personal interest.
Pages represents a significant step forward in automating the research and writing process, providing a powerful tool for anyone looking to produce well-structured and informative content with ease.
How Pages Works
Users begin by typing their topic or query into the prompt box. This can range from simple subjects to more complex research questions.
They can also tailor the writing to suit different audience types—beginners, experts, or a general audience. This selection influences the complexity and depth of the content.
Once the prompt is submitted, ‘Pages leverages Perplexity’s AI search models to perform several tasks. The AI scans the web for pertinent sources, ensuring that the gathered data is up-to-date and reliable.
Based on the collected information, ‘Pages’ generates the content, dividing it into logical sections. Each section is crafted to provide a coherent and comprehensive understanding of the topic.
To ensure credibility, the tool cites all sources used in the content, allowing users to verify the information and explore further.
‘Pages’ offers several customizations features to enhance user control over the final output. Users can specify the level of detail they desire in the content, from a high-level overview to an in-depth analysis.
The tool also includes relevant visuals to complement the text, which users can change to better suit their preferences or needs.
One of the current limitations of ‘Pages’ is its inability to directly edit the generated text. If users notice any errors or require changes, they must submit a revised prompt with the necessary corrections or adjustments.
The tool then regenerates the content based on the new prompt, aiming to address the specified issues.
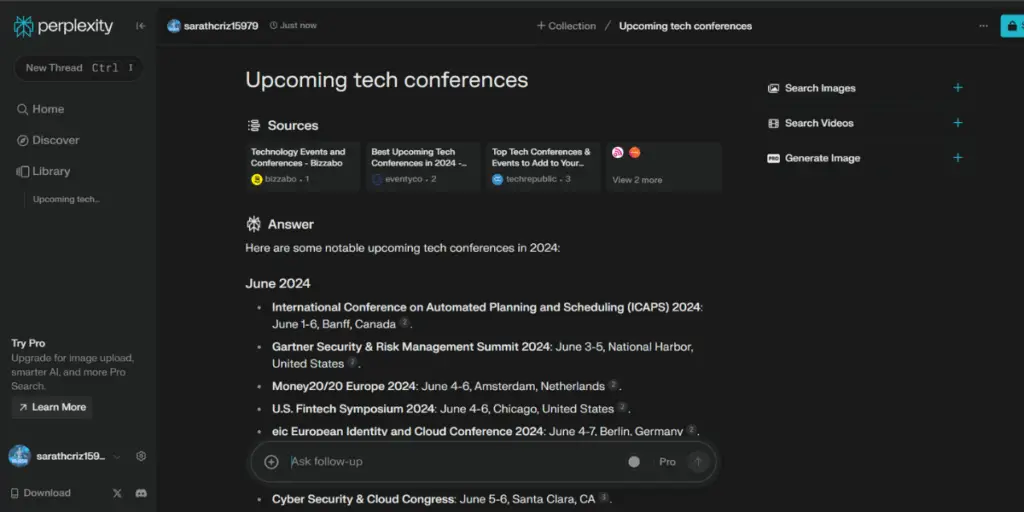
To test the versatility of ‘Pages,’ The Verge conducted an experiment on the topic “convergence of quantum computing and artificial intelligence and its impact on society.”
The tool was asked to create reports for three different audience types: beginner, general audience, and expert. For beginners, ‘Pages’ provided simplified explanations and introductory sources like blog posts from IBM and Wikipedia.
For a general audience, it offered a balanced approach with moderate use of technical jargon and diverse sources. For experts, the tool generated in-depth content with advanced sources and specialized terminology.
The results varied based on the audience type, demonstrating the ability of the ‘Pages’ to tailor content according to the user’s needs, though with noted limitations in handling highly complex topics.
Versatility and Performance
To assess the versatility and performance of ‘Pages,’ The Verge conducted an experiment using a complex topic called “convergence of quantum computing and artificial intelligence and its impact on society.”
This evaluation aimed to see how well ‘Pages’ handles intricate subjects and caters to different audience types: beginners, general readers, and experts.
For the beginner audience, the tool generated a report using simplified language and basic sources. The content included introductory blog posts from IBM and information from Wikipedia, making it accessible and easy to understand for those new to the topic.
For a more general audience, ‘Pages’ produced a balanced report with moderate technical jargon and a mix of diverse sources.
This version aimed to be informative without being overly simplistic or overly complex. The expert-level report used advanced sources and specialized terminology, targeting readers with a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
The Verge’s experiment highlighted several key points regarding ‘Pages” performance and versatility. The primary difference between the reports for various audiences was the complexity of language and the type of sources used.
The tool effectively adjusted its content to match the intended audience’s knowledge level. It used more basic explanations for beginners and more detailed technical information for experts.
While ‘Pages’ did a commendable job explaining the basics of quantum computing and AI, it struggled with providing in-depth analysis.

For the beginner-level report, the content was clear and straightforward, making it ideal for those unfamiliar with the topic.
Despite its innovative approach, ‘Pages’ showed limitations in handling advanced topics. For example, in the expert-level report on the convergence of quantum computing and AI, the tool included content about quantum inflection points, which was not directly related to the given prompt.
This indicates that while ‘Pages’ can effectively cover fundamental concepts, it may miss the mark on more nuanced aspects of complex subjects.
The differentiation in audience targeting also extended to the selection of sources. For beginner-level reports, ‘Pages’ relied on easily understandable sources such as blog posts and Wikipedia entries.
Limitations
The tool’s AI-driven approach sometimes struggles to maintain accuracy and relevance in more complex subject areas.
For instance, when tasked with generating an expert-level report on the convergence of quantum computing and artificial intelligence ‘Pages’ included unrelated content about quantum inflection points—a topic not directly relevant to the prompt.
This indicates that while ‘Pages’ can handle basic explanations and surface-level information effectively, it may falter with in-depth, specialized research.
One significant challenge is ensuring the specificity and relevance of the content generated. ‘Pages’ occasionally includes information that, while related to the general field, does not align precisely with the user’s query.
This issue can detract from the overall quality and usefulness of the report, particularly for users who require highly focused and accurate information.
A major drawback of ‘Pages’ is the inability to directly edit the generated text. Users cannot make on-the-fly corrections or adjustments to the content.
They must submit a new prompt to address any errors or to refine the information. This process can be cumbersome, especially when minor edits are needed.
The lack of direct editing capability limits the flexibility and efficiency of the tool, making it less suitable for users who need precise control over their content.
While ‘Pages’ excels at providing a broad overview and introductory information, it falls short in delivering detailed, in-depth research.
For advanced topics requiring comprehensive analysis, the tool’s output often lacks the necessary depth. This limitation makes ‘Pages’ less effective for producing highly detailed reports or academic papers where thorough research and nuanced understanding are critical.
The quality and relevance of the generated content are heavily dependent on the sources the AI selects. ‘Pages’ tend to use easily accessible and general sources, such as Wikipedia and popular blog posts, for beginner-level reports.
While this is useful for providing a general overview, it can be inadequate for expert-level content. The reliance on such sources can result in oversimplified information. It may not meet the standards required for professional or academic work.
Although ‘Pages’ is designed to assist a wide range of users, from educators to researchers and hobbyists, its current limitations make it less ideal for some groups.
For instance, researchers and educators who need detailed, accurate, and editable reports may find ‘Pages’ insufficient for their needs. Conversely, students or hobbyists looking for quick and easy information might benefit more from the tool’s capabilities.
Future updates to ‘Pages’ could include enhanced AI algorithms to improve the AI’s ability to understand and maintain the relevance of complex topics.
Potential Use Cases
Students can use ‘Pages’ to generate comprehensive study guides on various topics, helping them prepare for exams and understand complex subjects.
The tool can also assist students in quickly compiling reports and projects, ensuring they meet deadlines with well-structured content.
Educators can create detailed lesson plans and teaching materials, making complex concepts more accessible to their students.
In professional research, researchers and academics can leverage ‘Pages’ for preliminary research on new topics, helping lay the groundwork for more detailed studies.
The tool can compile summaries of existing research, aiding in the preparation of literature reviews for academic papers.
Academics can generate well-organized presentations for conferences and seminars, saving time on content creation.
Hobbyists and enthusiasts can use ‘Pages’ to quickly generate informative blog posts on topics of interest, sharing their knowledge with a broader audience.
Individuals working on personal projects can document their progress and findings, creating professional-looking reports.
In business applications, professionals and enterprises can use ‘Pages’ to conduct market research, compiling data and insights into comprehensive reports.
Companies can create detailed training materials for their employees, ensuring consistent and thorough knowledge transfer. Professionals can prepare customized presentations for clients, showcasing their expertise and insights.
To address the current limitations and enhance the tool’s capabilities, several future improvements can be made.
Enhancing AI algorithms to improve contextual understanding and handle advanced topics more effectively would ensure that all generated content is highly relevant to the prompt and provide more in-depth and accurate analysis.
Allowing users to directly edit the generated content would facilitate on-the-fly corrections and refinements, making the tool more flexible and user-friendly.
Introducing an interactive editing interface would enable users to tweak and customize the text, ensuring it meets their specific needs.
Expanding the AI’s research capabilities to provide more thorough and detailed reports suitable for advanced academic and professional use would be beneficial.
Connecting ‘Pages’ with academic databases and professional journals to access high-quality sources would enhance the depth and accuracy of the content.
Implementing a system to prioritize high-quality and reliable sources, ensuring the accuracy and credibility of the information, and allowing users to input specific sources or databases for the AI to pull information from would further tailor the content to user requirements.


