Google DeepMind introduces the Scalable, Instructible, Multiword Agent, an AI that transcends traditional boundaries by understanding and executing human language instructions across diverse 3D virtual environments.
This innovative agent is not confined to mastering single tasks or navigating predefined paths; instead, it showcases an unparalleled ability to adapt, learn, and apply its understanding in a variety of settings, from the intricate worlds of No Man’s Sky to the destructible environments of Teardown.
SIMA represents a significant step forward in the quest for AI that can seamlessly interact with and respond to human guidance, mirroring human-like adaptability and understanding through its development.
DeepMind not only pushes the envelope in AI research but also illuminates the path toward creating more general, versatile agents capable of assisting in an array of tasks, gaming and beyond. SIMA’s development, capabilities, and the potential it holds for the future of AI-driven interaction in virtual and real-world applications.
The Evolution of AI in Gaming
AI in gaming was primarily focused on creating opponents or environments that could challenge human players in predictable, rule-based games. The breakthrough came with DeepMind’s work on Atari games.
When AI began to learn and adapt to the gameplay through reinforcement learning, a type of machine learning, this was a foundational shift, moving from pre-programmed behaviours to AI that could learn strategies and improve over time.
The world watched in awe as AlphaGo, another DeepMind innovation, defeated world champions in Go, a game known for its deep strategic complexity and vast number of possible moves.
AlphaGo’s success was a testament to the power of deep learning and neural networks, demonstrating that AI could master tasks once thought to require uniquely human intuition and creativity.
Building on this legacy, DeepMind’s journey into AI and gaming has now culminated in the development of SIMA. Unlike its predecessors, which excelled in specific games, SIMA is designed to be a generalist agent.
It can interpret natural-language instructions and translate them into actions across multiple 3D virtual environments. This leap from specialized to generalist AI agents in gaming mirrors the broader aspirations of the AI research community—to develop systems that can understand and operate in the complex, nuanced, and ever-changing real world.
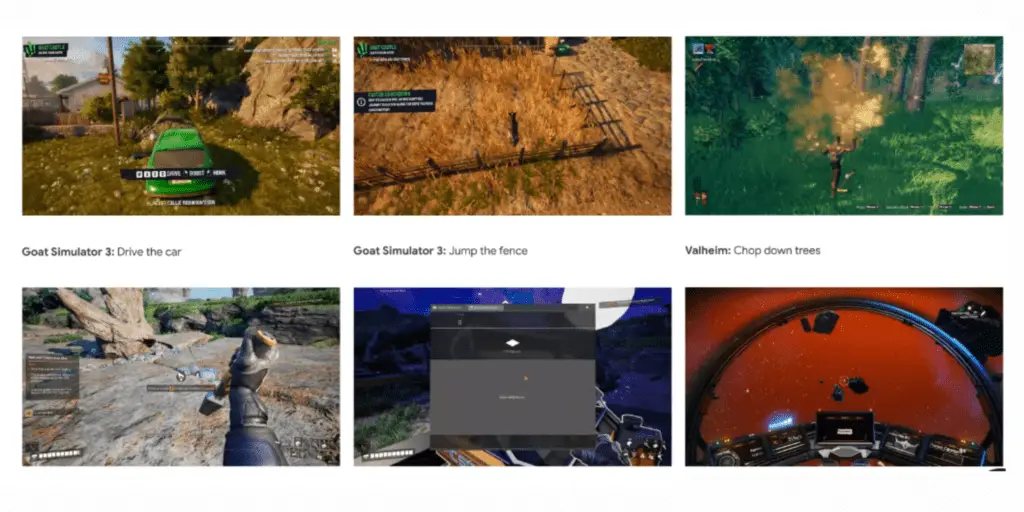
SIMA’s training across nine different video games, in partnership with eight-game studios, underscores the scale and ambition of this project.
From navigating the infinite galaxies of No Man’s Sky to the physics-based destruction of Teardown, SIMA is being taught to adapt, learn, and apply its understanding in an array of digital universes.
This is not just about achieving high scores or mastering a single game; it’s about creating an AI that can follow instructions, learn from interactions, and carry out tasks in a manner akin to a human being.
The evolution of AI in gaming, epitomized by the development of SIMA, is a testament to the field’s growth and its increasingly sophisticated understanding of artificial intelligence. It highlights the potential of AI to not only entertain and challenge but also to serve as a versatile tool for exploration, learning, and interaction within and beyond the gaming world.
As we stand on the cusp of new advancements, the journey of AI in gaming continues to inspire, promising even more revolutionary breakthroughs in the years to come.

SIMA’s Development and Training
DeepMind’s approach to developing SIMA involved forging partnerships with eight different game studios, thereby securing a rich and varied set of environments for training.
Among these were notable titles like “No Man’s Sky” by Hello Games and “Teardown” by Tuxedo Labs, each offering unique challenges that range from complex navigation and resource gathering to advanced activities like crafting and piloting spaceships.
This diversity is crucial for training an AI to adapt and apply its learning across different scenarios, mirroring the way humans can transfer knowledge and skills from one context to another.
In addition to commercial video games, SIMA’s training incorporated four research environments, including a bespoke environment developed with Unity called the Construction Lab.
This lab challenges the agent to build sculptures from building blocks, testing its skills in object manipulation and understanding of the physical world. These controlled environments are vital for honing specific capabilities that can be abstracted and applied to a broader range of tasks in commercial games.
A novel aspect of SIMA’s training methodology is its reliance on human gameplay and instructions. By recording gameplay sessions and the accompanying verbal instructions from human players, DeepMind created a dataset that bridges the gap between human language and in-game actions.
This method allows SIMA to learn not just the mechanics of gameplay but also how these actions correspond to real-world language instructions, enabling a more intuitive interaction between the agent and human users.
At the core of SIMA lies a sophisticated model architecture that combines pre-trained vision models with a main model capable of interpreting images, predicting video outcomes, and making decisions.
This architecture is fine-tuned on the specific 3D settings of the games in its portfolio, allowing SIMA to navigate and interact with complex virtual environments effectively.
SIMA operates using the same inputs a human would use: on-screen images and user-provided instructions, without the need for direct access to a game’s source code or APIs. SIMA’s performance is evaluated across a wide range of basic skills, including navigation, object interaction, and menu usage.
This evaluation not only demonstrates SIMA’s proficiency in executing specific tasks but also its potential to tackle more complex, multi-step objectives that mimic real-world problem-solving and strategic planning.
The development and training of SIMA illustrate DeepMind’s commitment to advancing AI research and its application. By focusing on generalization and adaptability, SIMA stands at the forefront of a new generation of AI agents capable of navigating the myriad challenges of virtual environments with unprecedented sophistication and versatility.
Capabilities and Performance of SIMA
One of the most significant capabilities of SIMA is its ability to interpret instructions given in natural language and execute the corresponding tasks within various video games and virtual environments.
This breakthrough is achieved through sophisticated model architectures that integrate pre-trained vision and video prediction models with a deep understanding of language.
This integration allows SIMA to perceive its environment, understand the task at hand, and take the necessary actions to complete it, bridging the gap between human communicative methods and machine execution.
SIMA’s versatility is demonstrated through its training and testing on a wide array of video games, each presenting different challenges and requiring a unique set of skills.
From navigating the procedurally generated universes of “No Man’s Sky” to executing precise destruction in “Teardown,” SIMA has shown a remarkable ability to adapt its learned skills to new and unfamiliar settings.
Its evaluation across 600 basic skills—including navigation, object interaction, and menu usage—highlights its proficiency and potential to understand and interact within any virtual environment it encounters.
The evaluation of SIMA’s capabilities has not been limited to simple tasks. DeepMind’s ambition is for SIMA to tackle tasks that require high-level strategic planning and the completion of multiple sub-tasks, such as finding resources and building a camp.
This direction points to a future where AI can not only assist in straightforward activities but also engage in complex problem-solving scenarios that mirror human-level strategic thinking.
A defining aspect of SIMA’s performance is its ability to generalize its learning across different games and environments. This ability was put to the test in a series of evaluations where SIMA demonstrated superior performance compared to specialized agents trained on individual games.
SIMA trained on a set of games showed nearly as proficient performance on an unseen game as on those it was trained on, indicating a significant step towards creating AI with a robust capability for generalization.
SIMA’s reliance on language not only for receiving instructions but also as a medium for learning and adaptation underscores the critical role of natural language processing in the development of versatile AI agents.
In scenarios where SIMA was not given language instructions, its behaviour, while appropriate, lacked the goal-directed focus that language training provided, illustrating the profound impact of linguistic context on AI performance.
The capabilities and performance of SIMA represent a monumental leap forward in the quest to create AI agents that can understand and act on human instructions across a multitude of virtual environments.
As SIMA continues to evolve, its development offers a glimpse into a future where AI can seamlessly integrate into our digital and physical worlds, assisting with tasks ranging from simple to complex, all through the power of language and adaptive learning.
The Future Potential of SIMA
SIMA’s ability to understand and execute complex instructions in 3D environments lays the foundation for next-generation gaming experiences.
Imagine multiplayer games where SIMA agents can participate as dynamic teammates or adversaries, capable of understanding strategy, adapting to player behavior, and even engaging in dialogue.
This could revolutionize online gaming, making AI-controlled characters indistinguishable from human players in terms of their adaptability and responsiveness.
The versatility and adaptability of SIMA make it an ideal candidate for simulation-based training and education. Its ability to operate in detailed virtual environments can be leveraged for realistic simulations in fields such as medicine, aviation, and disaster response.
Trainees can interact with SIMA agents to simulate complex scenarios that require critical thinking and strategic planning, enhancing the learning experience through a cost-effective and scalable solution.
SIMA’s proficiency in interpreting natural language and executing tasks in virtual environments presents significant opportunities for enhancing accessibility.
By integrating SIMA-like technologies into software and virtual interfaces, individuals with physical disabilities could navigate and interact with digital environments more intuitively, using voice commands to control and manipulate applications and games, thereby reducing barriers to digital content.
In the realm of content creation and design, SIMA’s capabilities can be harnessed to streamline workflows and bring creative visions to life with unprecedented efficiency.
Architects, game designers, and filmmakers could use SIMA to populate virtual worlds with intelligent agents that interact with the environment and each other, creating dynamic simulations and visualizations directly from verbal or written instructions.
Beyond traditional gaming, SIMA holds the promise of creating entirely new forms of interactive entertainment and storytelling.
With its ability to understand complex narratives and perform a wide range of actions, SIMA could enable interactive movies or narrative experiences where viewers influence the story through natural-language commands, leading to personalized and immersive entertainment experiences.
As DeepMind continues to refine and expand SIMA’s capabilities, the boundary between AI and human intelligence in virtual environments will increasingly blur, offering a glimpse into a future where AI agents can learn, adapt, and collaborate with humans across diverse realms of activity.
The ongoing development of SIMA not only showcases the potential for more instructable, generalist AI but also underscores the importance of ethical considerations and safeguards to ensure these technologies enhance human capabilities without unintended consequences.
The future potential of SIMA is a testament to the transformative power of AI, promising to redefine our interaction with digital worlds and expand the horizons of what is possible in gaming, education, accessibility, and beyond.

Final thoughts
The development of SIMA by Google DeepMind represents not just a milestone in the evolution of artificial intelligence within the gaming industry but also a beacon for the broader application of AI technologies.
As we venture into a future augmented by SIMA and similar AI innovations, it’s imperative to consider the broader implications of these technologies, as well as the challenges and opportunities they present.
The advancement of AI agents capable of interpreting and acting on natural language in complex environments raises important ethical questions. As these agents become more integrated into daily life, the need for transparent, responsible AI practices becomes paramount.
Ensuring that these technologies are developed and deployed in a manner that respects privacy, security, and ethical guidelines is crucial to mitigating potential risks, including biases and unintended consequences of AI actions.
SIMA’s development heralds a new era of human-AI collaboration, where AI agents can assist, entertain, and work alongside humans across a variety of contexts.
This collaboration has the potential to revolutionize industries by enhancing creativity, efficiency, and accessibility. However, it also necessitates a reevaluation of skills and roles within the workforce, highlighting the importance of adaptability and lifelong learning in the digital age.
While SIMA’s ability to generalize across different virtual environments is impressive, achieving similar levels of adaptability in the real world presents significant challenges. The complexity and unpredictability of real-world environments demand further advancements in AI’s understanding of context, physics, and social norms.
Continuing to improve these capabilities while ensuring AI’s actions are safe and beneficial is an ongoing challenge for researchers. The journey of SIMA underscores the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in pushing the boundaries of what AI can achieve.
The integration of linguistics, cognitive science, computer vision, and other fields will be essential in developing AI that can understand and navigate the world with the nuance and flexibility of human intelligence. This holistic approach to AI development promises to accelerate progress towards truly generalist agents.
The unveiling of SIMA by Google DeepMind is a testament to the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence and its potential to transform not only gaming but also many other aspects of society.
As we look to the future, the possibilities are as vast as they are exciting, promising a world where AI can enhance human capabilities, foster creativity, and open new avenues for interaction and exploration.
Realizing this potential will require careful navigation of the ethical, technical, and societal challenges that accompany such powerful technologies. In this journey, the development of SIMA stands as a milestone, marking the path towards a more interactive, adaptable, and collaborative future between humans and AI.


